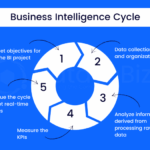
How to create a business intelligence strategy is essential for any organization looking to leverage data for informed decision-making. In an era where data is abundant, understanding how to transform this wealth of information into actionable insights is crucial. This guide will walk you through the fundamental components of a successful business intelligence strategy, providing the necessary tools and frameworks to navigate the complex landscape of data analytics.
From understanding the core principles of business intelligence to assessing your company’s unique needs, we’ll explore how to effectively design, implement, and evaluate a robust strategy that aligns with your business goals. Whether you’re a seasoned executive or a newcomer to the field, this comprehensive approach will help you harness the true power of your data.
Understanding Business Intelligence
Business intelligence (BI) refers to a set of technologies, strategies, and methodologies that transform raw data into meaningful insights to support better business decision-making. In a corporate context, BI encompasses the processes of collecting, analyzing, and presenting business data to provide historical, current, and predictive views of operations. This comprehensive approach enables organizations to gain a competitive edge, optimize performance, and enhance strategic planning.The significance of data-driven decision-making cannot be overstated.
In an era where information is abundant, leveraging data effectively allows businesses to identify trends, uncover insights, and make informed choices. Organizations that harness the power of data-driven decisions experience improved operational efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased profitability. According to a report by McKinsey, companies that utilize data-driven strategies are 23 times more likely to acquire customers, 6 times more likely to retain customers, and 19 times more likely to be profitable.
Types of Business Intelligence Tools
A variety of business intelligence tools are available to organizations, each serving different purposes and functions. Understanding these tools is essential for effectively implementing a BI strategy. The following categories of BI tools can be utilized:
- Data Visualization Tools: These tools help in representing data in graphical formats, making it easier to identify patterns and trends. Examples include Tableau and Power BI.
- Reporting Tools: These are designed to generate reports from various data sources, allowing users to analyze and share findings. Tools like Crystal Reports and Google Data Studio fall into this category.
- Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) Tools: OLAP tools enable users to perform multidimensional analysis of business data, providing insights through complex calculations. Examples include Microsoft SQL Server Analysis Services and Oracle Essbase.
- Data Mining Tools: These tools analyze large datasets to discover patterns and relationships, often used for predictive analytics. Notable tools include RapidMiner and KNIME.
- Dashboard Tools: Dashboards provide a visual interface for monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and other vital metrics. Examples are Domo and Klipfolio.
Selecting the right mix of these tools is crucial for a successful business intelligence strategy. Organizations should consider their specific needs, data sources, and desired outcomes when making these choices. Integrating these various BI tools into a cohesive strategy allows businesses to leverage data effectively, ensuring they remain agile and responsive to changing market conditions.
“Data is the new oil. It’s valuable, but if unrefined, it cannot really be used.” – Clive Humby
Ensuring data quality in business intelligence is crucial for making informed decisions. To achieve this, businesses must implement rigorous data validation processes and continuously monitor data integrity. A comprehensive approach to how to ensure data quality in business intelligence can help organizations maintain accurate datasets, ultimately leading to better insights and strategies.
Assessing Business Needs: How To Create A Business Intelligence Strategy

In establishing a robust business intelligence (BI) strategy, understanding and assessing business needs is paramount. This process involves identifying the specific objectives that drive the implementation of BI tools and systems. By thoroughly analyzing the current data landscape and integrating stakeholder requirements, organizations can better align their BI initiatives with business goals, ensuring that the solutions developed meet the actual demands of the organization.The assessment phase is crucial because it lays the groundwork for creating a tailored BI strategy that supports decision-making processes and enhances performance.
Measuring the success of business intelligence initiatives involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs). These key metrics for measuring business intelligence success allow organizations to evaluate their effectiveness in data usage, ensuring that insights lead to actionable outcomes and sustained growth.
Organizations need to take a systematic approach to evaluate their existing data capabilities and understand the needs of various stakeholders. This will help in creating a BI strategy that is not only effective but also sustainable.
Objectives for Implementing a Business Intelligence Strategy
Identifying the main objectives for a BI strategy is essential for guiding the overall implementation process. Some key objectives include improving decision-making, enhancing operational efficiency, and gaining competitive advantages. Clear objectives help stakeholders understand the purpose behind BI initiatives, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively. The following are common objectives organizations might pursue:
- Enhancing Data-Driven Decision-Making: Establishing BI tools that provide actionable insights to support informed decisions.
- Increasing Operational Efficiency: Streamlining processes and optimizing resource allocation through data analysis.
- Improving Customer Insights: Leveraging data to gain a deeper understanding of customer preferences and behaviors.
- Identifying Market Trends: Utilizing analytics to spot emerging trends that can inform strategic planning.
Analyzing the Current Data Landscape
A comprehensive analysis of the current data landscape is critical for determining how well existing systems meet business needs. This involves assessing the quality, accessibility, and relevance of data across the organization. Stakeholders’ requirements must also be considered to ensure that the BI strategy is aligned with their expectations. Key components to evaluate include:
- Data Quality: Evaluating accuracy, completeness, and consistency of the data collected.
- Data Accessibility: Assessing how easily stakeholders can access the data they need for analysis.
- Relevance of Data: Ensuring that the data aligns with the business goals and provides meaningful insights.
- Integration Capabilities: Determining how well existing systems communicate with each other to provide a cohesive data environment.
“A well-structured data landscape lays the foundation for effective BI solutions that drive organizational success.”
Checklist for Evaluating Existing Data Sources and Systems
Creating a checklist to evaluate existing data sources and systems helps organizations identify gaps and opportunities for improvement. This checklist serves as a practical tool for ensuring that all critical aspects of data management are considered during the assessment phase. Key items to include in the checklist are:
- Inventory of Data Sources: List all current data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and third-party applications.
- Data Governance Policies: Review existing data governance frameworks to ensure compliance and security.
- Stakeholder Feedback: Collect input from users regarding their data needs and pain points.
- Performance Metrics: Analyze current performance indicators to measure the effectiveness of existing systems.
By following this structured approach to assess business needs, organizations can effectively lay the groundwork for a successful business intelligence strategy that addresses both current challenges and future growth opportunities.
Designing the Strategy Framework
Creating an effective business intelligence (BI) strategy framework is essential for organizations aiming to leverage data for decision-making and operational efficiency. This framework acts as a blueprint that guides BI initiatives, ensuring that they align with the organization’s overall objectives and respond to its specific needs.The critical components of a business intelligence strategy include the data infrastructure, technology tools, governance policies, and the analytics framework.
Each of these components plays a vital role in ensuring that the BI strategy is robust, scalable, and capable of delivering actionable insights.
Critical Components of a Business Intelligence Strategy
A solid BI strategy consists of several interconnected elements that collectively support its effectiveness. Understanding these components is crucial for organizations to build a coherent and efficient BI framework. The following are key elements that should be integrated into any BI strategy:
- Data Infrastructure: The backbone of any BI strategy is a well-structured data infrastructure, which includes data warehouses, databases, and data lakes. This ensures that data is stored, managed, and retrieved efficiently.
- Technology Tools: A variety of analytical tools, visualization software, and reporting platforms are necessary to turn raw data into meaningful insights. Tools such as Tableau, Power BI, or QlikView are common choices across industries.
- Governance Policies: Establishing governance policies ensures data quality, security, and compliance. This includes data stewardship roles, access controls, and data usage policies that align with legal and ethical standards.
- Analytics Framework: An analytics framework determines how data will be analyzed. This can range from descriptive analytics to advanced predictive models, based on organizational needs.
Examples of Successful Business Intelligence Frameworks
Various industries have successfully implemented business intelligence frameworks that demonstrate the power of data-driven decision-making. These frameworks showcase how organizations can tailor their BI strategies to meet specific challenges and opportunities.In the retail sector, Walmart employs a sophisticated BI framework that integrates real-time sales data and inventory management systems. This allows Walmart to optimize its supply chain and enhance customer experience by ensuring product availability.In the healthcare industry, organizations like Mount Sinai Health System utilize BI to improve patient outcomes.
Their framework leverages data analytics to identify trends in patient care, helping to streamline operations and enhance service delivery.The financial services industry also exemplifies effective BI practices. JPMorgan Chase utilizes advanced analytics to detect fraudulent transactions in real-time, ensuring the security of customer accounts while improving operational efficiency.
Aligning Business Intelligence Goals with Overall Business Objectives
To achieve a successful BI strategy, it is essential to align BI goals with the broader business objectives of the organization. This alignment ensures that BI initiatives support the overall mission and vision of the company, leading to more impactful outcomes.Establishing a clear connection between BI goals and business objectives can be achieved through the following methods:
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving key stakeholders from different departments helps identify the specific data needs and goals that align with each department’s objectives.
- Performance Metrics: Defining clear performance indicators that reflect both BI and business objectives fosters accountability and helps measure success effectively.
- Continuous Feedback Loop: Implementing a feedback mechanism allows organizations to adjust their BI strategy based on changing business needs and market conditions.
- Integrated Planning: Incorporating BI into the strategic planning process ensures that data insights influence key business decisions and strategy formulation.
Implementation and Execution
The successful implementation and execution of a business intelligence (BI) strategy is critical for organizations aiming to turn data into actionable insights. This phase requires meticulous planning and coordination among various stakeholders to ensure that the BI tools and processes align with the organizational goals. By following a structured approach, businesses can effectively roll out their BI initiatives and foster a data-driven culture.
Steps for Rolling Out a Business Intelligence Strategy, How to create a business intelligence strategy
Implementing a BI strategy involves several key steps that ensure the effective deployment of tools and processes within the organization. The following steps Artikel a comprehensive approach:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Establish specific, measurable goals that the BI strategy aims to achieve, such as improving decision-making, enhancing operational efficiency, or increasing sales.
2. Select BI Tools
Choose appropriate BI tools that meet the defined objectives and are compatible with existing systems. Consider factors such as user-friendliness, scalability, and integration capabilities.
3. Plan Data Integration
Develop a data integration plan to gather and consolidate data from various sources, ensuring data quality and consistency. This step may involve data cleansing and transformation processes.
4. Create a Deployment Timeline
Establish a timeline for the rollout of BI tools and processes, including milestones and checkpoints to monitor progress.
5. Pilot Testing
Conduct pilot tests with a select group of users to identify any issues or challenges with the tools before a full-scale rollout. Gather feedback to make necessary adjustments.
6. Full-Scale Implementation
Roll out the BI strategy organization-wide, ensuring that all users have access to the tools and necessary resources to utilize them effectively.
7. Performance Monitoring
Continuously monitor the performance of BI tools and processes to ensure they are meeting the defined objectives. Make adjustments as needed to optimize performance.
Training Employees on Business Intelligence Tools
Training is a fundamental component of successful BI implementation. Employees must be equipped with the necessary skills to utilize BI tools effectively. A structured training program should encompass the following aspects:
Identify Training Needs
Assess the current skill levels of employees and determine the specific training needs related to the BI tools being implemented.
Develop Training Materials
Create comprehensive training materials, including user manuals, video tutorials, and quick reference guides, tailored to different user groups.
Conduct Hands-On Workshops
Organize interactive workshops where employees can practice using the BI tools in a controlled environment to build their confidence and competence.
Offer Ongoing Support
Establish a robust support system that includes access to BI experts or a help desk team that can assist employees with any questions or challenges they encounter.
Encourage Knowledge Sharing
Foster a culture of knowledge sharing among employees by setting up forums or discussion groups where users can exchange tips and best practices.
Importance of Ongoing Support and Maintenance for BI Systems
The deployment of a business intelligence strategy does not end with implementation; ongoing support and maintenance are crucial for long-term success. Key aspects include:
Regular System Updates
Ensure that BI tools are regularly updated to incorporate new features and enhancements, as well as to address security vulnerabilities.
User Feedback Mechanisms
Create channels for users to provide feedback on the BI tools, enabling continuous improvement based on real-world usage experiences.
Performance Reviews
Conduct regular performance reviews of the BI systems to identify areas for optimization and ensure alignment with evolving business needs.
Training Refreshers
Provide periodic refresher training sessions to keep employees updated on new features and best practices, reinforcing their skills and knowledge.
Data Governance Practices
Establish data governance practices to maintain the integrity, security, and compliance of the data being used in BI processes.By meticulously executing these steps and ensuring robust training and ongoing support, organizations can effectively harness the power of business intelligence to drive informed decision-making and achieve strategic objectives.
Measuring Success and Iteration
Measuring the success of business intelligence (BI) initiatives is critical for validating their effectiveness and ensuring that they align with organizational goals. By establishing robust mechanisms to evaluate performance, businesses can adapt and refine their strategies to better meet the needs of their stakeholders. This process not only involves the identification of key performance indicators (KPIs) but also encompasses continuous feedback loops and reporting mechanisms that demonstrate value.
Key Performance Indicators for Business Intelligence
Defining KPIs is essential for assessing the impact of business intelligence initiatives. KPIs provide measurable values that reflect the success of a business in achieving its objectives. Effective KPIs for BI might include:
- User Adoption Rate: Measures the percentage of employees actively using BI tools to make data-driven decisions.
- Data Accuracy: Evaluates the reliability of the data presented in BI reports, which is critical for trust in the insights derived.
- Time to Insight: Assesses how quickly actionable insights can be derived from data, reflecting the efficiency of BI processes.
- Cost Savings: Quantifies the financial benefits resulting from improved decision-making and operational efficiencies driven by BI.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculates the financial return generated from BI initiatives relative to their costs.
These indicators help organizations gauge the effectiveness of their BI strategies and align them with broader business objectives.
Gathering Feedback for Iterative Improvements
To ensure that BI strategies remain effective and relevant, it is necessary to gather feedback continuously from users and stakeholders. This feedback loop enables organizations to identify areas for improvement and optimize their BI initiatives. Effective methods for gathering feedback include:
- User Surveys: Conducting regular surveys can provide insights into user satisfaction, challenges, and suggestions for enhancements.
- Focus Groups: Engaging small groups of users to discuss their experiences can yield qualitative data that highlights specific issues and opportunities.
- Usage Analytics: Analyzing user interaction with BI tools helps identify patterns and areas where additional training or adjustments are needed.
- Stakeholder Meetings: Regular check-ins with key stakeholders can ensure alignment and capture insights on organizational needs and changing dynamics.
By incorporating user feedback into the BI strategy, organizations can make iterative improvements that enhance the overall effectiveness and user experience of their BI initiatives.
Reporting Results and Showcasing Value
Communicating the results of business intelligence initiatives to stakeholders is crucial for maintaining support and demonstrating value. Effective reporting methods include:
- Dashboards: Interactive dashboards provide real-time data visualization, making it easier for stakeholders to understand insights at a glance.
- Performance Reports: Regularly generated reports summarizing key metrics and progress against KPIs help keep stakeholders informed about the impact of BI initiatives.
- Case Studies: Presenting specific examples where BI has led to successful outcomes can illustrate its tangible benefits and ROI.
- Workshops and Presentations: Hosting sessions to present findings and insights encourages dialogue and fosters a culture of data-driven decision-making.
These methods ensure that stakeholders are not only kept in the loop but are also aware of the strategic value that business intelligence brings to the organization, fostering continued investment and engagement in BI initiatives.