How to implement big data in business is a crucial question for modern enterprises navigating an increasingly data-driven landscape. As organizations strive to harness vast amounts of data, understanding its essence and potential becomes paramount. Big data encompasses diverse forms, from structured databases to unstructured social media streams, each carrying valuable insights that can propel a business forward.
In today’s competitive environment, leveraging big data effectively enables companies to optimize operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation. This guide will explore not only the foundational concepts of big data but also practical steps to identify specific business needs, implement cutting-edge technologies, and ensure robust data governance.
Understanding Big Data
In today’s fast-paced business environment, the term “big data” is frequently mentioned, yet many still struggle to comprehend its full implications. Understanding big data is crucial for businesses aiming to harness its power to drive innovation and efficiency. From customer behavior analytics to operational optimization, big data has the potential to transform how companies operate and compete.Big data refers to the vast volumes of data generated every second, encompassing various formats and sources.
Its defining characteristics, often referred to as the “three Vs,” include volume, velocity, and variety. Volume denotes the immense amounts of data generated, ranging from terabytes to petabytes. Velocity highlights the speed at which data is collected and processed, crucial for real-time decision-making. Variety signifies the different types of data—structured, unstructured, and semi-structured—that organizations must manage.
Types of Big Data
Understanding the different types of big data is essential for effective data management and analysis. Each type presents unique challenges and opportunities, influencing how businesses approach data utilization. The following are the primary categories of big data:
- Structured Data: This type of data is highly organized and easily searchable, typically found in relational databases and spreadsheets. Examples include customer names, addresses, and transaction details. The clarity of structured data facilitates straightforward analysis and reporting.
- Unstructured Data: Unstructured data lacks a predefined format, making it more complex to analyze. It includes text, images, videos, and social media content. For instance, customer reviews and social media posts provide valuable insights but require sophisticated tools to extract meaningful information.
- Semi-Structured Data: This data type falls between structured and unstructured data. It contains elements of both, featuring tags or markers to separate data elements. Examples include XML and JSON files, which allow for easier data parsing and analysis while still maintaining a level of ambiguity.
The importance of big data in today’s business landscape cannot be overstated. Companies leveraging big data can gain insights that drive better decision-making and enhance operational efficiency. For example, retail giants use big data analytics to understand shopping patterns, optimize inventory management, and personalize marketing strategies, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and increasing sales.
Businesses that effectively utilize big data are better equipped to stay ahead of the competition and adapt to changing market dynamics.
Choosing the right database management system is crucial for any project. Factors such as scalability, performance, and ease of integration play a significant role. To navigate this complex decision-making process, you can refer to this comprehensive guide on how to choose the right database management system for projects that simplifies the selection process based on your specific needs.
>Identifying Business Needs

To successfully implement big data within a business, understanding and identifying specific business needs is paramount. This process involves assessing the current challenges and opportunities that big data can address, aligning data initiatives with organizational goals, and ensuring that the right data sources are leveraged for maximum impact.A thorough assessment of business needs requires both qualitative and quantitative methods. Engaging stakeholders across various departments can provide insights into operational inefficiencies, customer behavior, and market trends that big data can help illuminate.
This collaborative approach not only fosters a sense of ownership but also reveals the areas where data analytics can significantly enhance decision-making processes.
Methods to Assess Business Needs
Utilizing a structured approach to assess business needs lays the groundwork for effective big data implementation. Here are several methods to consider:
- Stakeholder Interviews: Conduct interviews with key stakeholders to gather insights into specific pain points and expectations from data initiatives.
- SWOT Analysis: Perform a SWOT analysis to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to current data usage and potential big data strategies.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Deploy surveys to collect quantitative data on what departments perceive as their biggest challenges and how they could leverage big data solutions.
- Focus Groups: Facilitate focus group discussions to explore ideas and brainstorm solutions, enhancing collaboration among different business units.
Determining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for measuring the effectiveness of big data applications. KPIs help in quantifying the success of implemented strategies and ensuring alignment with business objectives.
Key Performance Indicators Enhanced by Big Data
Identifying KPIs that can be influenced by big data assists organizations in tracking improvements and justifying data investments. Important KPIs include:
- Customer Acquisition Cost: Analyze customer data to optimize marketing strategies and reduce acquisition costs.
- Customer Lifetime Value: Use predictive analytics to estimate the long-term value of customers and guide retention efforts.
- Operational Efficiency: Measure process efficiencies through data-driven insights, reducing waste and improving productivity.
- Market Share Growth: Utilize data analytics to identify market trends and consumer preferences, driving informed strategic decisions.
The selection of appropriate data sources is crucial for ensuring that the organization retrieves relevant and reliable information to drive insights.
Determining the Right Data Sources
Choosing the right data sources is a critical step in the big data implementation process. The following considerations can help in this determination:
- Internal Data: Assess existing internal data repositories, such as CRM systems, ERP systems, and transaction logs, which often contain valuable insights.
- External Data: Explore external data sources such as market research reports, social media insights, and public datasets that can enrich internal data.
- Real-Time Data Streams: Consider integrating real-time data sources like IoT devices and online customer interactions to capture timely insights for immediate decision-making.
- Structured vs. Unstructured Data: Evaluate the types of data required for analysis, balancing the use of structured data with unstructured data sources like text, images, and videos for comprehensive insights.
By thoroughly assessing business needs, identifying appropriate KPIs, and determining the right data sources, organizations can establish a solid foundation for their big data initiatives, ultimately enhancing their strategic capabilities and operational efficiency.
Implementing Big Data Technologies

The implementation of big data technologies is essential for businesses aiming to leverage large volumes of data for insights and competitive advantage. Selecting the right tools and establishing a strong infrastructure are critical steps in this process. This section will delve into popular technologies, a step-by-step guide for setting up a big data ecosystem, and a comparison of cloud versus on-premises solutions.
Popular Big Data Technologies and Tools
To effectively manage and analyze vast amounts of data, several technologies and tools have gained prominence in the big data landscape. These tools provide various capabilities, from data storage to real-time processing. Understanding their functionalities can help businesses choose the right ones for their needs. Key technologies include:
- Hadoop: An open-source framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using simple programming models. Hadoop is known for its scalability and fault tolerance.
- Apache Spark: A unified analytics engine for big data processing, known for its speed and ease of use. Spark supports batch processing, stream processing, and machine learning, making it versatile for various applications.
- NoSQL Databases: Such as MongoDB and Cassandra, these databases are designed to handle unstructured data and provide high availability, scalability, and flexibility.
- Apache Kafka: A distributed event streaming platform capable of handling trillions of events a day, Kafka is essential for real-time data processing and integration between different systems.
- Data Warehousing Solutions: Tools like Amazon Redshift and Google BigQuery are designed for analyzing large datasets quickly. They provide SQL-like interfaces for ease of use and efficient querying.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up a Big Data Ecosystem
Establishing a big data ecosystem requires a systematic approach. A well-structured setup can facilitate seamless data ingestion, storage, processing, and analysis. Below is a step-by-step guide to help businesses implement a big data ecosystem effectively.
- Define Business Goals: Clearly Artikel what you want to achieve with big data analytics. This could include improving customer insights, optimizing operations, or enhancing product offerings.
- Identify Data Sources: Determine the types of data you need, which could be internal (sales records, customer interactions) or external (social media, market research).
- Choose the Right Tools: Based on the data volume and processing needs, select appropriate big data technologies from the popular tools discussed earlier.
- Design Data Architecture: Plan how data will flow through your ecosystem, including ingestion, storage, processing, and visualization. Ensure scalability and security are considered.
- Implement Data Storage Solutions: Set up data storage systems, such as Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) for structured and unstructured data.
- Establish Data Processing Framework: Use Apache Spark or Hadoop MapReduce for processing data efficiently. Configure these frameworks according to your data characteristics.
- Set Up Data Analytics Tools: Deploy tools for data visualization and analytics. Solutions like Tableau or Power BI can help convert data into actionable insights.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor system performance and data processing efficiency. Make adjustments and optimizations as needed.
Comparison of Cloud vs. On-Premises Solutions for Big Data Infrastructure
When establishing a big data infrastructure, businesses can choose between cloud-based solutions or on-premises setups. Each option has distinct advantages and considerations that can impact overall performance and cost.
When it comes to large applications, optimizing database performance is essential for ensuring smooth user experiences. Effective strategies include indexing, query optimization, and proper schema design. For detailed insights and techniques, check out this resource on how to optimize database performance for large applications to enhance your application’s efficiency.
| Criteria | Cloud Solutions | On-Premises Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go model, potentially lowering upfront costs. | Higher initial investment required for hardware and software. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to accommodate growing data needs. | Scaling can be limited and requires additional hardware purchases. |
| Maintenance | Managed by cloud providers, reducing internal workload. | Requires in-house IT resources for maintenance and updates. |
| Security | Providers implement robust security measures but may raise concerns over data privacy. | Greater control over security, but requires significant investment in safeguards. |
| Performance | Dependent on internet speed; can experience latency. | Typically offers consistent performance as data is stored on-site. |
Data Management and Governance: How To Implement Big Data In Business
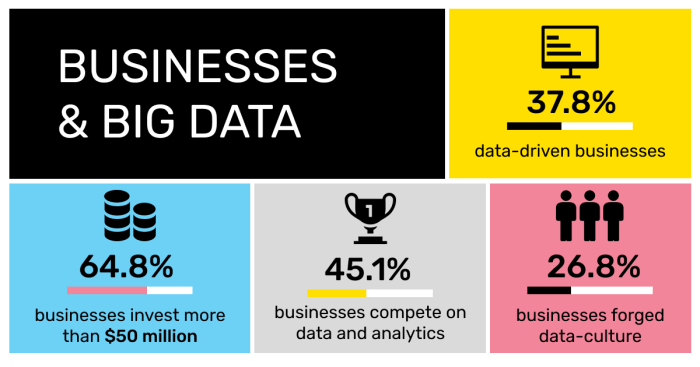
Data management and governance are pivotal in harnessing the power of big data for business success. Properly managing data allows organizations to extract valuable insights while maintaining the integrity and security of their information. In this section, we will explore best practices for effective data management, emphasize the significance of data quality and governance, and Artikel strategies for compliance with data protection regulations essential in today’s data-driven landscape.
Best Practices for Data Management in Big Data Scenarios
Implementing best practices in data management ensures that organizations can effectively store, process, and analyze vast amounts of data. Here are key practices to consider:
- Data Classification: Organize data into categories based on sensitivity and importance. This ensures that critical data receives the necessary protection and attention.
- Data Integration: Utilize tools that enable seamless integration of data from various sources. This promotes a unified view of information, facilitating better decision-making.
- Data Lifecycle Management: Establish processes for managing data from its creation to its disposal. This includes archiving and deleting outdated information to maintain efficiency.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic audits of data management practices to identify areas for improvement. This helps in ensuring compliance and optimizing data workflows.
- Collaboration Between Departments: Encourage cross-departmental collaboration to ensure that data usage aligns with business objectives. This fosters a culture of data-driven decision-making.
Importance of Data Quality and Governance in Big Data Projects, How to implement big data in business
Data quality and governance are essential components of successful big data projects. High-quality data enhances the reliability of insights derived from analytics, while effective governance frameworks ensure that data is managed responsibly.
“The accuracy, completeness, and timeliness of data directly impact the decision-making process in organizations.”
Ensuring data quality involves implementing validation procedures, such as data cleansing and enrichment, to maintain data integrity over time. Governance, on the other hand, involves defining policies for data usage, ownership, and accountability. This clarity reinforces a strong data culture, where all stakeholders understand their roles in maintaining data quality.
Strategies for Ensuring Compliance with Data Protection Regulations
Compliance with data protection regulations is critical to safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining customer trust. Organizations should adopt several strategies to ensure adherence to these regulations:
- Data Encryption: Utilize encryption techniques to protect sensitive data both in transit and at rest, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Implement stringent access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information. Role-based access control (RBAC) is a useful method.
- Regular Training: Conduct ongoing training programs for employees on data protection practices and compliance requirements. This fosters a culture of data responsibility.
- Data Minimization: Collect only the data that is necessary for business operations. This reduces risk and simplifies compliance efforts.
- Incident Response Plans: Develop and maintain an incident response plan to address potential data breaches. This should include communication protocols and remediation steps.
Real-World Applications of Big Data
The transformative power of big data has been vividly demonstrated across various industries. Companies are increasingly leveraging big data to enhance operational efficiency, drive marketing strategies, and improve customer service. By understanding and implementing big data technologies, organizations can extract valuable insights from vast datasets, ultimately leading to informed decision-making and competitive advantages.
Case Studies of Successful Big Data Implementations
Several organizations have successfully implemented big data strategies, showcasing the potential benefits and applications. Notable examples include:
- Netflix: By utilizing big data analytics, Netflix delivers tailored content recommendations based on user preferences and viewing history. This approach not only enhances user experience but also significantly boosts engagement and retention rates.
- Amazon: Amazon employs big data to optimize supply chain management and personalize marketing efforts. Through extensive data analysis, they can forecast demand, manage inventory, and provide personalized shopping experiences, resulting in increased sales and customer satisfaction.
- Walmart: Walmart harnesses big data to enhance its logistics and inventory management processes. By analyzing consumer behavior and purchasing trends, Walmart can predict demand fluctuations and streamline operations, leading to significant cost savings.
Leveraging Big Data Insights for Decision-Making
Big data enables organizations to make data-driven decisions that can enhance operational performance and strategic planning. The insights gained from data analysis can influence various aspects of business operations, including:
- Predictive Analytics: Businesses apply predictive analytics to anticipate future trends based on historical data. This helps in inventory management, risk assessment, and resource allocation.
- Market Segmentation: By analyzing customer data, companies can identify distinct segments within their target market, allowing for more tailored marketing strategies that resonate with specific consumer needs.
- Performance Monitoring: Organizations can utilize big data for real-time monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs). This facilitates quick adjustments to strategies and operations as needed, maintaining competitiveness in the market.
Innovative Uses of Big Data in Marketing, Customer Service, and Operations
The innovative applications of big data are reshaping marketing, customer service, and operational efficiency. Some notable innovations include:
- Targeted Advertising: Big data allows brands to create highly targeted advertising campaigns by analyzing consumer behavior and preferences. This increases the effectiveness of advertisements and boosts ROI.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Companies leverage big data to predict customer issues and proactively address them. For instance, chatbots powered by big data analytics can provide real-time assistance, improving customer satisfaction.
- Operational Efficiency: Big data analytics can identify inefficiencies within business processes. Companies use data-driven insights to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance productivity.
“Data is the new oil.” This phrase underscores the immense value that big data brings to modern businesses, enabling them to refine their strategies and drive success.


