How to integrate business intelligence with existing systems sets the stage for a transformative journey in the ever-evolving business landscape. As organizations strive to harness data-driven insights for competitive advantage, the integration of robust business intelligence tools with pre-existing systems emerges as a critical endeavor. This process not only enhances decision-making but also aligns with overall business strategies, paving the way for sustainable growth and improved operational efficiency.
In today’s data-centric world, understanding the various integration strategies is essential. From ensuring data management and governance to assessing technology compatibility, the successful incorporation of business intelligence requires a comprehensive approach. Moreover, user adoption and ongoing training play pivotal roles in maximizing the potential of integrated systems. By measuring success through well-defined KPIs, organizations can continuously refine their processes and strategies.
Integration Strategies: How To Integrate Business Intelligence With Existing Systems
Integrating business intelligence (BI) tools with existing systems is essential for organizations aiming to enhance their data-driven decision-making capabilities. Successful integration not only improves data accessibility but also streamlines processes and drives better business outcomes. This section explores various strategies for achieving effective integration, showcases successful case studies, and emphasizes the importance of aligning BI goals with overarching business strategies.
Integration Approaches
Organizations can adopt several strategies to effectively integrate BI tools with their existing systems. Each strategy has its unique advantages and can be tailored to meet specific business needs.
In today’s competitive landscape, understanding the importance of data visualization in business intelligence is crucial for organizations. Effective data visualization helps businesses to convey complex information clearly and quickly, enabling decision-makers to grasp insights and trends at a glance. This capability not only enhances strategic planning but also boosts operational efficiency by turning raw data into actionable insights.
- APIs and Middleware: Utilizing Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) allows for seamless communication between different systems. Middleware solutions can facilitate data transfer and ensure compatibility between legacy systems and modern BI tools.
- Data Warehousing: Implementing a centralized data warehouse enables organizations to consolidate data from various sources. This approach simplifies data access for BI tools, ensuring that users have a single source of truth.
- Real-Time Data Integration: Adopting real-time data integration techniques ensures that BI tools access the most current data available. This strategy is crucial for organizations needing to respond swiftly to market changes or internal performance metrics.
- Custom Development: For organizations with unique needs, custom development can provide tailored solutions that integrate BI tools with existing systems. This approach often involves significant investment but can yield high returns in terms of efficiency and usability.
Successful Integration Case Studies
Several organizations have successfully integrated BI tools into their existing systems, leading to enhanced data insights and improved operational efficiency.
- Retail Chain: A leading retail chain implemented an API-based integration strategy to connect its inventory management system with a BI tool. This real-time integration allowed for accurate stock level monitoring, leading to a 20% reduction in overstock and improved sales forecasting.
- Financial Services Firm: A financial services firm adopted a data warehousing approach, consolidating data from multiple departments. By integrating BI tools, the firm achieved a unified view of customer data, resulting in more personalized services and a 15% increase in customer retention rates.
- Healthcare Provider: A healthcare provider utilized real-time data integration to connect its electronic health records system with BI tools. This integration led to quicker access to patient data, improving care coordination and reducing hospital readmission rates by 10%.
Importance of Aligning BI Goals with Business Strategy
Aligning BI initiatives with overall business strategy is crucial for maximizing the value derived from data analytics. When BI goals are in sync with the organizational mission, it fosters a culture of data-driven decision-making across all levels.
- Strategic Alignment: Ensuring that BI objectives support the broader business goals enhances focus and resource allocation, resulting in more effective data initiatives.
- Enhanced Collaboration: When teams understand how BI tools contribute to strategic objectives, it encourages collaboration and enhances the adoption of data-driven practices throughout the organization.
- Performance Measurement: Aligning BI goals with business strategy facilitates better measurement of performance metrics, enabling organizations to track progress effectively and make informed adjustments.
Data Management and Governance
Effective data management and governance are foundational elements for successful integration of business intelligence (BI) within existing systems. In a landscape increasingly driven by data, organizations must prioritize the systematic handling and oversight of data to unlock insights and facilitate informed decision-making. By establishing robust data management practices and governance policies, companies can ensure that their BI initiatives deliver accurate, timely, and actionable information.In integrating BI with existing systems, it is crucial to establish a framework that encompasses data quality, consistency, and compliance across all platforms.
The importance of managing data effectively cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the reliability of analytics and reporting. Below are best practices and techniques to enhance data management and governance.
Choosing the right tools is vital for any business looking to harness the full potential of data analytics. When considering how to choose business intelligence tools effectively , businesses must evaluate their specific needs, the scalability of the tools, and integration capabilities. A well-selected BI tool can streamline operations and empower teams to make informed decisions that drive growth and innovation.
Best Practices for Data Management
Implementing best practices in data management is essential for maintaining the integrity and utility of data. These practices include:
- Data Inventory and Classification: Conduct a comprehensive inventory of data assets across systems. Classify data based on its sensitivity, relevance, and compliance requirements to ensure appropriate handling and security.
- Data Integration Techniques: Employ effective data integration methods such as ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes or data virtualization to harmonize data from disparate sources. This enhances accessibility and usability across BI tools.
- Regular Data Audits: Conduct periodic audits of data to identify discrepancies, eliminate redundancies, and enhance accuracy. This practice aids in maintaining a high standard of data quality over time.
Ensuring Data Quality and Consistency
Data quality and consistency are vital for accurate analysis and reporting in business intelligence. The following techniques can be employed to achieve high standards:
- Validation Rules: Implement validation rules during data entry to ensure data integrity. This includes checks for format, completeness, and adherence to predefined standards.
- Data Cleansing Processes: Establish ongoing data cleansing protocols that automatically identify and rectify errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies. This continuous improvement process is essential for reliable BI outputs.
- Master Data Management (MDM): Adopt MDM practices to create a single, authoritative source of critical business data. This mitigates the risks associated with conflicting data across systems.
Governance Policies for Effective BI Integration
A comprehensive set of governance policies is essential for overseeing data management efforts in a BI context. These include:
- Data Ownership and Stewardship: Assign clear ownership and stewardship roles to ensure accountability for data quality and compliance. This facilitates responsibility and oversight at various organizational levels.
- Access Control Policies: Develop robust access control measures to regulate who can view and manipulate data. This protects sensitive information and ensures compliance with relevant regulations.
- Compliance and Regulatory Policies: Implement policies that ensure adherence to legal and regulatory frameworks governing data privacy and protection. This is critical in avoiding potential legal pitfalls and maintaining customer trust.
Establishing strong data management and governance practices is not just about compliance; it enables organizations to leverage data as a strategic asset for competitive advantage.
Technology Compatibility
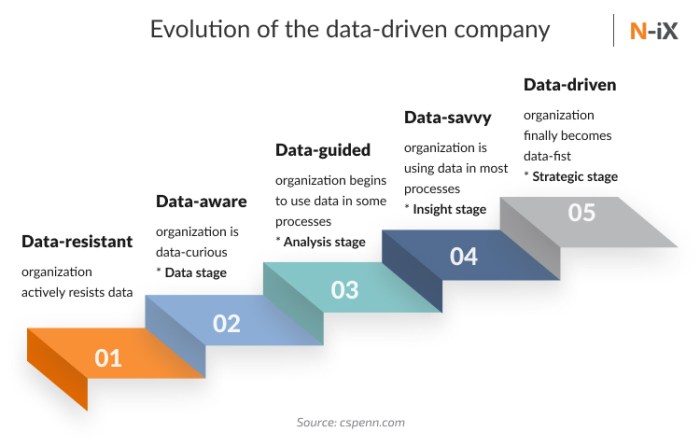
Assessing technology compatibility is a crucial step when integrating business intelligence (BI) tools with existing systems. Understanding how these tools will interact with current software and infrastructure can significantly reduce implementation challenges and improve overall efficiency. Organizations must ensure that their chosen BI solutions can seamlessly connect with legacy systems, databases, and applications to leverage data effectively.Evaluating technology compatibility involves a thorough examination of the technical specifications and integration capabilities of BI tools and existing systems.
This assessment should consider factors such as data formats, APIs, software architecture, and overall infrastructure compatibility. Businesses can use this information to make informed decisions about which BI solutions will best fit their technology environment.
Checklist for Evaluating Integration Platforms and Tools
When considering integration platforms and tools, a structured evaluation can streamline the selection process. The following checklist Artikels key factors that should be assessed to ensure compatibility and functionality:
- Integration Capabilities: Verify if the tool supports various data sources, including cloud and on-premises systems.
- API Availability: Check for robust APIs that facilitate communication between systems.
- Data Transformation Features: Evaluate the ability of the tool to transform data into compatible formats for analysis.
- User Interface: Assess the usability of the integration tool for both technical and non-technical users.
- Scalability: Ensure the tool can accommodate future data growth and additional integrations.
- Security Standards: Verify compliance with industry security standards to protect sensitive data during integration.
- Vendor Support: Consider the level of support offered by the vendor for integration challenges.
Addressing these aspects can help organizations select a BI integration tool that aligns with their technological landscape.
Common Challenges Faced During Integration and Solutions, How to integrate business intelligence with existing systems
Integrating business intelligence tools into existing systems often comes with its share of challenges. Recognizing these obstacles and implementing effective solutions is vital for a successful integration process. Common challenges include data silos, compatibility issues, and resistance from users accustomed to existing systems.To combat these issues, consider the following solutions:
- Data Silos: Implement a centralized data warehouse to consolidate data from disparate sources, fostering a unified view for BI tools.
- Compatibility Issues: Conduct thorough compatibility assessments and leverage middleware solutions that bridge gaps between different technologies.
- User Resistance: Invest in training programs to familiarize staff with new BI tools, highlighting their benefits to encourage adoption.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Optimize data processing and storage solutions to ensure that integration does not slow down existing systems.
- Change Management: Develop a change management strategy to guide the organization through the transition, addressing concerns and providing ongoing support.
By proactively identifying these challenges and applying targeted solutions, organizations can enhance their integration efforts, resulting in a more efficient and effective business intelligence environment.
User Adoption and Training
Integrating business intelligence tools into existing systems is just the beginning; ensuring that employees adopt these tools is crucial for their success. Effective user adoption and comprehensive training programs can significantly enhance the utility of these systems, ultimately driving better decision-making and business outcomes.A well-structured training program is essential to facilitate user adoption across different departments and roles within the organization.
Tailoring training to specific user groups helps address varying levels of expertise and usage contexts. The following strategies highlight methods to encourage user adoption and design effective training initiatives.
Methods for Ensuring User Adoption of New Business Intelligence Tools
User adoption hinges on engagement and ease of use. A few key strategies can effectively foster a culture of adoption among employees:
- Involve Users Early: Engage potential users during the implementation phase to gather feedback and set expectations. This involvement fosters a sense of ownership and acceptance.
- Communicate Benefits: Clearly articulate how the new tools will improve current workflows, increase efficiency, and support decision-making processes, thereby motivating users to adapt.
- Provide Ongoing Support: Establish a support system that includes helpdesk services, user groups, and forums where users can seek help and share experiences.
Designing a Training Program Tailored for Different User Groups
A one-size-fits-all approach often fails in training programs. Instead, a diverse training program can be developed to cater to the unique needs of various user groups such as executives, analysts, and general staff. Essential components of such a program include:
- Executive Training: Focus on strategic insights and high-level analytics. Consider offering workshops that demonstrate how BI tools can inform executive decision-making.
- Analyst Training: Provide in-depth training on data manipulation, reporting, and visualization techniques. A mix of hands-on sessions and theoretical learning can enhance their analytical skills.
- General Staff Training: Offer simplified tutorials that emphasize basic functionalities and user-friendly navigation to ensure that all employees feel comfortable using the tools.
Creating User-Friendly Interfaces to Facilitate Ease of Use
Intuitive user interfaces are critical in encouraging the use of business intelligence tools. A well-designed interface can significantly lower the barriers to user adoption. Key elements to consider when developing user-friendly interfaces include:
- Simplicity in Design: Focus on a clean layout with easily accessible features. Avoid clutter that can overwhelm users and detract from essential functionalities.
- Customization Options: Allow users to personalize their dashboards to suit individual preferences and workflows, enhancing the relevance of the tools to their tasks.
- Interactive Elements: Incorporate interactive elements such as drag-and-drop features and tooltips that guide users through unfamiliar processes, promoting self-sufficiency.
“An intuitive interface not only simplifies user interaction but also boosts overall productivity and satisfaction among employees.”
Measuring Success

Incorporating business intelligence into existing systems is a transformative endeavor that requires ongoing assessment to ensure its effectiveness. Successfully measuring the integration’s impact is essential for optimizing business operations and driving strategic growth. The right performance indicators, regular reviews, and a commitment to continuous improvement can create a robust framework for evaluating success.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establishing measurable outcomes is critical for evaluating the success of business intelligence integration. Key performance indicators (KPIs) serve as quantitative benchmarks that provide insights into various aspects of performance. The following KPIs are crucial in measuring success:
- Data Accuracy: The percentage of data entries that are correct, reflecting the quality of input and processing.
- User Engagement: The frequency and duration of user interactions with the BI tools, indicating usability and relevance.
- Decision-Making Speed: The average time taken to make strategic decisions post-integration, showcasing efficiency improvements.
- Return on Investment (ROI): The financial returns generated from BI initiatives relative to the costs incurred for integration and maintenance.
- Adoption Rate: The percentage of users actively utilizing BI tools compared to the total number of intended users, which reflects user acceptance.
Regular Reviews and Updates
Conducting regular reviews of the integration process is essential to ensure that the business intelligence system remains aligned with organizational goals. This involves assessing performance against established KPIs and making necessary adjustments based on the findings. A structured review process should include:
- Monthly Performance Assessments: Regularly evaluate performance metrics to identify trends and areas needing attention.
- Quarterly Strategy Meetings: Discuss insights gained from BI data and adjust business strategies accordingly.
- Annual Integration Audits: Comprehensive evaluations of the BI integration to identify persistent issues and opportunities for enhancement.
- Stakeholder Feedback Sessions: Gather insights and recommendations from users to inform updates and changes.
Continuous Improvement Framework
Building a framework for continuous improvement based on user feedback and performance metrics ensures that the business intelligence system evolves with the organization’s needs. This proactive approach involves:
- Feedback Loops: Implement mechanisms for users to provide feedback on BI tools, ensuring their voices are heard and considered in future developments.
- Iterative Enhancements: Utilize feedback and performance data to inform incremental changes to the BI system, enhancing functionality and user experience over time.
- Training and Support: Provide ongoing training sessions and support resources to help users adapt to new features and improvements.
- Benchmarking Best Practices: Regularly compare the BI system’s performance with industry standards to identify gaps and opportunities for advancement.


