How to start a business intelligence project sets the stage for an enthralling narrative that delves into the intricacies of transforming data into actionable insights. This journey begins with a clear definition of project objectives and stakeholder roles, laying the groundwork for a successful initiative. As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, understanding the essential components of a business intelligence project becomes crucial for harnessing its full potential.
From selecting the right technology to ensuring data is clean and well-managed, each step plays a vital role in the overall success of the project. By thoroughly evaluating tools, preparing data strategically, and formulating a robust implementation strategy, businesses can set the stage for impactful analysis and informed decisions. The importance of continuous monitoring and evaluation cannot be overstated, as it allows teams to adapt and improve based on real-time feedback, creating a culture of ongoing enhancement.
Project Initiation: How To Start A Business Intelligence Project
The initiation phase of a business intelligence project is crucial as it sets the foundation for the entire endeavor. It involves outlining clear objectives, understanding the scope, and assembling a team to drive the project forward. Proper initiation ensures that the project aligns with organizational goals and meets the needs of its stakeholders effectively.Defining the objectives and scope of the business intelligence project allows for a focused approach and sets clear expectations.
The objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), guiding the project team throughout the implementation process. The project scope Artikels what will be included and excluded, helping to prevent scope creep and ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
Objectives and Scope Definition
Establishing clear objectives and a well-defined scope is essential for guiding business intelligence initiatives. The objectives should highlight what the organization aims to achieve, whether it’s improving decision-making, uncovering insights from data, or enhancing operational efficiency. The scope delineates the boundaries of the project, specifying the departments, processes, and data sources involved.For example, a project may aim to improve sales forecasting by analyzing historical sales data and market trends.
In defining the scope, it is important to identify the specific sales channels to be analyzed, the timeframe for analysis, and any limitations in data availability.
Stakeholder Identification and Roles
Identifying stakeholders and their respective roles is a pivotal element in the project initiation phase. Stakeholders can include data analysts, IT personnel, business leaders, and end-users who will interact with the business intelligence tools. Understanding their interests and contributions can foster collaboration and ensure their needs are met.The roles of stakeholders can be categorized as follows:
- Project Sponsor: Provides financial resources and overall project support.
- Project Manager: Oversees the project execution, ensuring timelines and budgets are adhered to.
- Data Analysts: Responsible for data interpretation and generating actionable insights.
- IT Support: Maintains the technical infrastructure and ensures data security.
- End-Users: Utilize the business intelligence tools to inform their decisions.
Effective communication among these stakeholders helps streamline the project and aligns individual contributions towards common goals.
Initial Data Requirements and Sources
Understanding initial data requirements and identifying potential sources of data is fundamental in the project initiation phase. A comprehensive assessment of the data landscape helps in determining what data is necessary to achieve project objectives.The initial data requirements may include:
- Historical sales data from CRM systems.
- Market research data from third-party providers.
- Internal operational data from ERP systems.
- Customer feedback and survey results.
Evaluating these data sources ensures that the project team can access reliable and relevant data for analysis, thereby enhancing the quality of insights generated.
“Quality data is the cornerstone of effective business intelligence.”
Understanding the significance of business law is crucial for any entrepreneur. It provides essential guidance on legal frameworks and regulations that govern commercial activities. To dive deeper into this subject, check out Hukum Bisnis Adalah: Panduan Lengkap Manfaat dan Solusi Bisnis , which offers comprehensive insights into the benefits and solutions related to business law.
In summary, the project initiation phase lays the groundwork for a successful business intelligence project by clearly defining objectives, engaging stakeholders, and identifying necessary data sources. This structured approach enables organizations to efficiently use their data and drive informed decision-making.
Technology Selection

Selecting the right technology is a critical step in the advancement of any business intelligence (BI) project. The appropriate tools and platforms can significantly impact the effectiveness of data analysis, reporting capabilities, and overall insights derived from data. It is essential to conduct a thorough evaluation of various BI tools to ensure they align with the specific needs and objectives of the organization.Evaluating different business intelligence tools and platforms requires a comprehensive understanding of their features and functionalities.
Each tool comes with unique strengths and weaknesses that can influence its suitability for a particular business context.
Evaluation and Comparison of BI Tools
When comparing BI tools, it is vital to thoroughly assess the key capabilities that differentiate them. Here is a list of important features to consider:
- Data Visualization: The ability to transform complex data into intuitive visual representations, such as dashboards and reports, is paramount. Effective visualization enhances comprehension and facilitates quicker decision-making.
- Data Integration: The capability to seamlessly connect with various data sources, including databases, cloud services, and APIs, is crucial for comprehensive analysis.
- User-Friendly Interface: A tool with an intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface fosters user adoption and lowers the learning curve for team members.
- Analytics Features: Advanced analytics capabilities, including predictive analytics and machine learning integration, can provide deeper insights and foresight.
- Collaboration Tools: Features that enable sharing insights and collaborating among team members can enhance group decision-making and foster a data-driven culture.
- Mobile Access: Support for mobile devices ensures that users can access insights on-the-go, which is increasingly important in a fast-paced business environment.
Selecting a business intelligence tool goes beyond just features; it involves understanding how well the tool can grow and adapt with the organization.
Importance of Scalability and Integration
Scalability is a vital attribute that determines a BI platform’s ability to adapt to growing data volumes and user needs. Organizations should prioritize tools that can scale up or down based on changing requirements without compromising performance.
“A scalable solution enables companies to manage increasing amounts of data without significant system overhauls.”
Integration capabilities are equally important, as they determine how well the BI tool can work with existing systems and new technologies. A robust integration framework allows businesses to leverage their current technology stack while adding new functionalities. This ensures that organizations can continue to adapt to technological advancements and changing business landscapes without costly disruptions.In summary, the selection of technology for a business intelligence project should be informed by a detailed evaluation of various tools, with a focus on essential features, scalability, and integration capabilities that support an organization’s long-term objectives and growth.
For businesses aiming to thrive, identifying key activities is vital. These activities form the backbone of any successful strategy, enabling companies to deliver value effectively. To learn more about effectively implementing these concepts, explore Aktivitas Utama dalam Kanvas Model Bisnis: Panduan Lengkap untuk Memahami dan Menerapkannya , which provides a thorough exploration of the essential components of a business model canvas.
Data Preparation
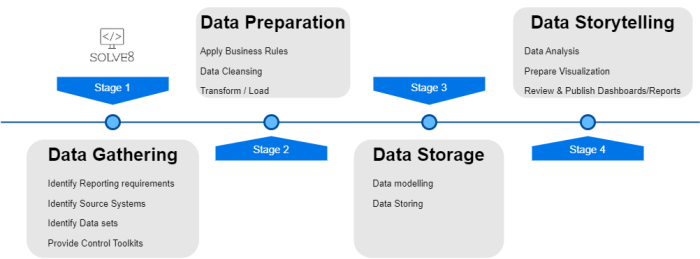
Data preparation is a critical phase in any business intelligence project, laying the groundwork for accurate analysis and actionable insights. This stage involves several meticulous steps to ensure that data is not only clean and reliable but also effectively stored and managed. Implementing a robust data preparation strategy sets the tone for successful BI operations and informed decision-making.
Data Cleaning and Transformation
The process of data cleaning and transformation is essential for mitigating inaccuracies and inconsistencies that can skew analysis results. Here are the necessary steps involved:
- Identifying Errors: Analyze the dataset to locate missing values, duplicates, and outliers that could distort outcomes.
- Correcting Inaccuracies: Rectify identified errors through methods such as imputation for missing values or removing duplicates.
- Standardization: Ensure consistency in data formats, such as date formats, currency symbols, and categorical values.
- Normalization: Adjust the range of numeric values to enhance comparability and eliminate bias.
- Data Transformation: Convert data into appropriate formats or structures, such as aggregating data for summary analysis or pivoting for easier reporting.
Data Storage and Management Strategy
An effective strategy for data storage and management is vital for accessibility and performance. This strategy should include:
- Database Selection: Choose an appropriate database system (e.g., SQL, NoSQL) based on data complexity and volume.
- Data Warehousing: Implement a data warehouse to centralize information from various sources, enhancing query performance and data retrieval.
- Backup Solutions: Establish regular backup protocols to safeguard against data loss and ensure continuity.
- Data Lifecycle Management: Define procedures for data archiving and purging to manage data growth efficiently.
Importance of Data Governance and Security Measures, How to start a business intelligence project
Data governance and security are paramount for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of business intelligence data. Effective governance frameworks ensure compliance and accountability within data management. Key aspects include:
- Data Quality Standards: Establish metrics and guidelines for maintaining high-quality data throughout its lifecycle.
- Access Controls: Implement user permission settings to restrict data access based on roles, ensuring sensitive information is protected.
- Compliance Regulations: Adhere to industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) to safeguard personal and sensitive data.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Regularly audit data activities and changes to identify potential security threats or governance lapses.
Implementing a comprehensive data governance strategy not only enhances data security but also improves decision-making processes.
In conclusion, meticulous data preparation through cleaning, effective storage management, and stringent governance is essential for the success of any business intelligence initiative, ultimately enabling organizations to harness their data for strategic advantage.
Implementation Strategy
The implementation strategy of a business intelligence project is crucial for ensuring that all phases and components are executed effectively. This stage includes developing a comprehensive timeline, training plans for users, and methods to gather feedback. Each of these elements plays a vital role in achieving the project’s goals and milestones.The first step in the implementation strategy is to create a timeline that Artikels the project phases and key milestones.
An effective timeline provides a roadmap for the project team and highlights critical deadlines, ensuring that tasks are completed in a timely manner.
Project Timeline and Milestones
A well-structured timeline helps in organizing the various tasks involved in the implementation of the business intelligence project. It facilitates communication among stakeholders and sets clear expectations. The timeline should include phases such as data integration, system testing, and user feedback sessions. The following are essential components to consider when creating a project timeline:
- Phase 1: Data Integration
-This phase involves connecting various data sources and ensuring data quality. It typically spans 4-6 weeks. - Phase 2: System Testing
-Testing the system for bugs and performance issues is crucial and usually takes 3-4 weeks. - Phase 3: User Training
-Training end-users and stakeholders on how to utilize the BI tools effectively can take 2-3 weeks. - Milestone Reviews
-Schedule regular milestone reviews every two weeks to assess progress and make necessary adjustments.
Training Plan for End-Users and Stakeholders
A comprehensive training plan is essential for ensuring that end-users and stakeholders can effectively utilize the business intelligence tools. This plan should cover various aspects, including tool navigation, data interpretation, and reporting functionalities. The training plan should include the following elements:
- Training Materials
-Develop user manuals, video tutorials, and FAQs to assist users in navigating the system. - Hands-on Workshops
-Conduct interactive workshops where users can practice using the BI tools in a controlled environment. - Feedback Mechanism
-Implement a feedback mechanism post-training to assess the effectiveness of training sessions and make improvements.
Iterative Testing and Feedback Methods
Iterative testing and feedback are critical for ensuring that the business intelligence solution meets the needs of its users. This approach allows for continuous improvements based on user experiences and data analysis.Key methods for conducting iterative testing and gathering feedback include:
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
-Involve end-users in testing the system before the final rollout to identify any issues or areas for enhancement. - Regular Feedback Sessions
-Schedule bi-weekly feedback sessions with stakeholders to gather insights on the functionality and usability of the BI tools. - Surveys and Questionnaires
-Distribute surveys after training sessions and initial usage to gather quantitative and qualitative feedback.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Effective monitoring and evaluation are critical components in measuring the success of any business intelligence project. Proper assessment of project outcomes not only determines the overall effectiveness of the initiative but also highlights areas for improvement and strategic adjustments moving forward. This systematic approach to evaluation ensures that a business intelligence project aligns with its intended goals while remaining adaptable to changing needs and user feedback.A robust framework for monitoring and evaluation involves establishing clear metrics and reporting mechanisms that can elucidate the value derived from the business intelligence project.
Metrics should reflect both quantitative and qualitative aspects, helping assess project performance comprehensively.
Key Metrics for Success Assessment
Establishing relevant metrics to gauge the success of a business intelligence project is essential. These metrics should encompass various dimensions of the project, including user engagement, data accuracy, and impact on decision-making processes. The following metrics are crucial in this assessment:
- User Adoption Rate: Measures the percentage of intended users actively engaging with the BI tools, indicating the relevance and usability of the project.
- Data Quality Index: Evaluates the accuracy, completeness, and timeliness of the data utilized, ensuring that decisions are based on reliable information.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculates the financial benefit derived from the BI project relative to its cost, providing insights into the project’s profitability.
- Improvement in Decision-Making Efficiency: Assesses the reduction in time taken for decision-making processes, illustrating the BI project’s influence on operational efficiency.
- User Satisfaction Score: Gathers feedback from users regarding their experience, revealing areas of strength and potential improvement in the BI tools.
Framework for Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is vital in ensuring that a business intelligence project remains relevant and effective. This can be achieved through a structured approach that integrates user feedback and performance metrics into ongoing project enhancements. The following steps Artikel a framework for continuous improvement:
- Regular User Surveys: Conduct frequent surveys to collect user feedback on the BI tools, which can highlight both strengths and potential areas for enhancement.
- Feedback Loops: Implement mechanisms for users to provide ongoing feedback, ensuring that their experiences and suggestions directly influence project evolution.
- Performance Reviews: Schedule periodic assessments of project success against established metrics to identify trends and areas needing attention.
- Agile Methodology: Utilize agile project management principles to allow for iterative improvements based on user feedback and changing business needs.
- Training and Support: Offer continuous education and support for users to enhance their engagement and ability to leverage BI tools effectively.
Regular Reporting Methods
Establishing clear reporting methods is essential for communicating findings and updates related to the business intelligence project. Regular reporting not only keeps stakeholders informed but also reinforces accountability and transparency throughout the organization. Consider the following reporting methods:
- Monthly Performance Dashboards: Create visual dashboards that summarize key metrics and trends, offering stakeholders a quick overview of project performance.
- Quarterly Review Meetings: Organize meetings to discuss project progress, key findings, and necessary adjustments, fostering a collaborative environment for stakeholders.
- Annual Impact Reports: Compile comprehensive reports detailing the project’s overall impact, including ROI, user satisfaction, and improvements in decision-making processes.
- Real-Time Alerts: Implement alerts for critical changes in data quality or user activity, enabling immediate response to potential issues.


