With how to visualize big data for insights at the forefront, we discover the transformative power of data visualization in today’s data-driven world. Visualizing big data not only makes complex information accessible but also empowers organizations to make informed decisions that can lead to success. As we delve into this topic, we’ll explore the methods, tools, and best practices that can unravel the mysteries hidden within large datasets.
As businesses grapple with ever-increasing volumes of data, translating this information into visual formats becomes crucial. Insightful visuals can simplify overwhelming data, reveal patterns, and help in crafting strategic decisions across various industries, from healthcare to finance. Join us as we navigate through essential techniques and tools that demystify the art of data visualization, ensuring clarity and insightfulness for all stakeholders involved.
Importance of Visualizing Big Data
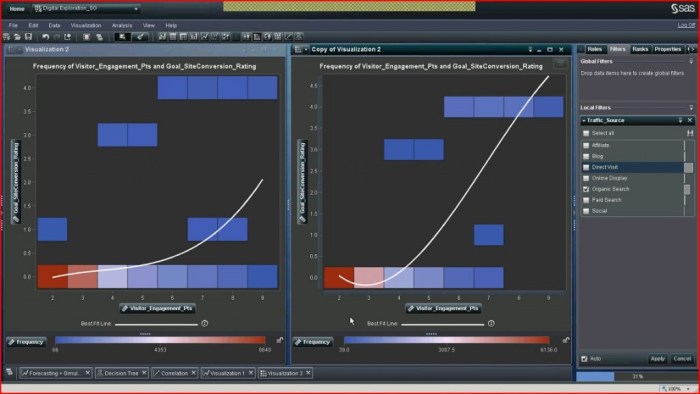
The visualization of big data is a critical process that transforms complex datasets into visual formats, allowing for easier comprehension and analysis. With the exponential growth of data, organizations are increasingly faced with the challenge of interpreting vast amounts of information. Effective visualization tools bridge the gap between raw data and actionable insights, enabling stakeholders to grasp intricate patterns and trends quickly.Data visualization significantly impacts decision-making processes within businesses.
To stay ahead in the fast-paced digital era, businesses are increasingly adopting big data technologies for real time processing. These technologies allow companies to analyze data as it streams in, enabling quick decision-making and responsiveness to market changes. By leveraging real-time insights, organizations can optimize their strategies and improve overall efficiency, ensuring they remain agile and competitive.
By translating numerical data and complex relationships into graphical representations, stakeholders can identify trends, correlations, and outliers that might otherwise go unnoticed. This capacity to rapidly understand and interpret data fosters informed decision-making and strategic planning, ultimately leading to improved business outcomes. For instance, companies leveraging visualization tools can enhance their marketing strategies by analyzing customer behavior patterns and preferences, leading to more targeted campaigns.
Industries Benefiting from Data Visualization
Numerous industries leverage data visualization for enhanced insights and operational efficiency. Below are some key sectors where visualization plays a vital role:
- Healthcare: Medical professionals use data visualization to track patient outcomes, manage hospital resources, and analyze treatment effectiveness. For example, visual dashboards can illustrate trends in patient admissions, highlighting peak times and informing staffing decisions.
- Finance: Financial analysts utilize visual tools to examine stock market trends, investment risks, and portfolio performance. Graphs and charts make it easier to identify market fluctuations, helping investors make timely decisions.
- Retail: Retailers employ data visualization to analyze sales performance, inventory levels, and customer purchasing patterns. By visually representing sales data, they can optimize inventory management and improve customer engagement strategies.
- Transportation: In the transportation sector, data visualization aids in route optimization and logistics management. Maps and flow charts can illustrate traffic patterns, leading to more efficient delivery schedules.
- Education: Educational institutions use data visualization to analyze student performance, attendance rates, and resource allocation. This enables schools to identify at-risk students and allocate resources effectively.
“Data visualization is the art of turning data into information, enabling businesses to see the bigger picture.”
In today’s data-driven world, understanding how big data impacts decision making is crucial for businesses. By harnessing vast amounts of information, organizations can make more informed choices, anticipate market trends, and enhance customer experiences. This analytical approach not only fosters innovation but also streamlines operations, ultimately driving success in a competitive landscape.
These examples illustrate how various industries capitalize on the power of data visualization to derive insights, streamline operations, and enhance decision-making processes. By presenting complex information in a visually digestible format, organizations can foster an environment that promotes data-driven strategies and innovation.
Methods of Data Visualization: How To Visualize Big Data For Insights
Visualizing large datasets effectively is crucial for deriving meaningful insights. Various methods exist, each tailored to different data types and audience needs. By employing the right visualization technique, one can transform complex data into compelling narratives that facilitate understanding and decision-making.Different visualization methods can be employed, including graphs, charts, and maps. Each method has its own unique strengths and weaknesses, making it essential to select the most appropriate one based on the specific characteristics of the data and the preferences of the target audience.
Types of Visualization Methods
The following are commonly used methods for visualizing large datasets, each suited for specific scenarios and outcomes:
- Bar Charts: Ideal for comparing quantities across different categories. They provide a straightforward visual comparison, especially when dealing with categorical data.
- Line Graphs: Effective for displaying trends over time. They highlight changes and patterns, making them suitable for time-series data.
- Pie Charts: Useful for illustrating proportions within a whole. However, they can become confusing with too many categories.
- Scatter Plots: Best for showing relationships between two quantitative variables. They can reveal correlations and outliers effectively.
- Heat Maps: Excellent for representing data density across geographic areas, showing patterns and intensity through color variations.
- Geospatial Maps: Effective for visualizing location-based data. These maps enhance geographical insights, especially in analytics involving demographics or resources.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Visualization Methods, How to visualize big data for insights
When choosing a visualization method, it is essential to understand their strengths and weaknesses. The following table presents a comparison of various techniques:
| Visualization Method | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Bar Charts | Clear display of categorical comparisons. | Less effective for large datasets with many categories. |
| Line Graphs | Good for showing trends over time. | Can be misleading if data points are not evenly spaced. |
| Pie Charts | Visually appealing for showing proportions. | Hard to read when there are multiple segments. |
| Scatter Plots | Effective for highlighting correlations. | Can become cluttered with too many data points. |
| Heat Maps | Visually intuitive for density analysis. | Color choices can mislead if not properly selected. |
| Geospatial Maps | Great for location-specific insights. | Requires accurate geographical data to be effective. |
Selecting the Right Visualization Technique
The process of selecting an appropriate visualization technique involves several steps, ensuring that the chosen method aligns with both the data type and the audience’s needs. The following steps Artikel this selection process:
- Identify the Data Type: Determine whether the data is categorical, continuous, or temporal, as this influences the visualization choice.
- Understand Your Audience: Analyze the audience’s level of expertise and familiarity with data to choose an appropriate complexity level.
- Define the Purpose: Establish what you aim to convey, whether it’s trends, comparisons, or distributions, guiding the visualization technique.
- Choose the Visualization Method: Based on the identified data type, audience understanding, and purpose, select the most suitable visualization method.
- Test and Iterate: Create preliminary visualizations and seek feedback, adjusting them based on input to enhance clarity and effectiveness.
By carefully evaluating these factors, one can create impactful visualizations that not only present data but tell a story that resonates with the intended audience.
Tools and Software for Visualization
In the world of big data, the ability to visualize information efficiently is crucial for deriving insights and making informed decisions. Various tools and software exist to assist analysts and businesses in transforming complex data into understandable visual formats. The choice of the right tool can significantly impact the way data is interpreted and utilized across organizations.Several popular tools are available for visualizing big data, each with unique features and capabilities that cater to different user needs and technical expertise.
Understanding these tools can guide users in selecting the best option for their specific requirements, whether that be simplicity, advanced functionality, or integrations with other systems.
Popular Data Visualization Tools
A selection of tools stands out for their effectiveness in visualizing big data. Each offers distinct features that enhance data representation, accessibility, and integration:
- Tableau: Renowned for its user-friendly interface, Tableau allows users to create interactive and shareable dashboards. Its strong data integration capabilities enable seamless connection to various data sources, including spreadsheets and cloud-based data. Users appreciate its drag-and-drop functionality that simplifies the design process.
- Power BI: Developed by Microsoft, Power BI is favored for its integration with existing Microsoft products. It provides robust business analytics tools for data visualization and sharing insights across an organization. Its natural language query capability is particularly praised, allowing users to interact with data using plain language.
- QlikView: Known for its associative data modeling engine, QlikView allows users to explore data freely. It offers powerful visualization options, enabling dynamic dashboard creation. Users highlight its capacity for real-time data processing, making it ideal for immediate insights.
- Google Data Studio: This free tool created by Google provides an easy entry point for users looking to visualize data in a customizable format. It allows integration with various Google products, facilitating access to data from Google Analytics and Sheets. Users commend its collaborative features, which support real-time sharing and editing.
- Apache Superset: This open-source software is designed for modern data exploration and visualization. Superset is praised for its ability to handle large datasets efficiently, offering a range of visualization options. Users value its flexibility and the capability to create custom visualizations through SQL queries.
User experiences with these tools often highlight case studies that showcase effective big data visualization. For instance, a retail company utilizing Tableau was able to visualize customer purchasing patterns, leading to enhanced inventory management and targeted marketing strategies. Similarly, a healthcare institution adopted Power BI to track patient data trends, resulting in improved patient care and operational efficiency. These examples underscore the importance of selecting the right tool to meet specific analytical needs and enhance overall data-driven decision-making within organizations.
Best Practices in Data Visualization
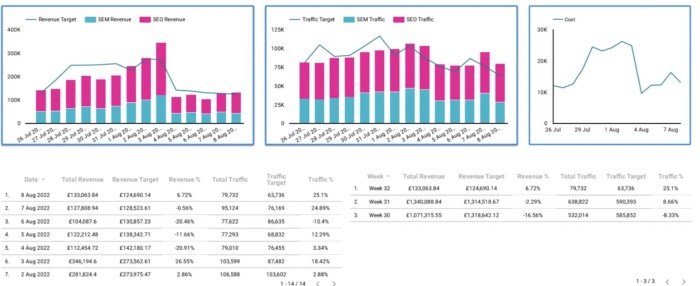
Creating effective visual representations of data is essential for communicating insights clearly and effectively. Following best practices in data visualization can significantly enhance the ability to convey complex information. It allows viewers to grasp trends, patterns, and anomalies quickly, making data-driven decisions easier.When preparing data visualizations, adhering to guidelines can help ensure clarity and accuracy. By considering the audience’s needs and the context in which the data will be presented, one can create visuals that are not only informative but also engaging.
Below are essential guidelines to follow, as well as a checklist of dos and don’ts to make your data visuals more effective.
Guidelines for Creating Effective Visual Representations
Several key principles should guide the creation of data visuals to enhance comprehension and reduce confusion. These guidelines include:
- Know Your Audience: Tailor your visuals to the knowledge level and interests of your audience, ensuring relevance and engagement.
- Choose the Right Type of Chart: Select visual formats that best represent the data type and the message being conveyed, such as line graphs for trends or bar charts for comparisons.
- Focus on Clarity: Use clear labels and legends, and avoid clutter. Each element in the visual should have a purpose.
- Maintain Consistency: Use a consistent color scheme, font style, and layout across visualizations to help users focus on the data rather than adjusting to different formats.
- Emphasize Key Insights: Highlight important data points or trends using colors or annotations to guide the viewer’s attention.
Checklist of Dos and Don’ts for Effective Data Visualization
Implementing a straightforward checklist can streamline the visualization process. Below is a compilation of dos and don’ts to maximize the effectiveness of your data visuals.
- Dos:
- Do use appropriate axes; ensure they are scaled correctly to avoid misleading interpretations.
- Do provide context by including relevant background information or additional data points.
- Do use interactive elements when suitable, allowing users to explore data in depth.
- Don’ts:
- Don’t overload visuals with too much information; simplicity is key.
- Don’t use misleading scales or visual effects that can distort the data representation.
- Don’t forget to cite data sources, ensuring credibility and transparency.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Data Visualization
Recognizing and avoiding common pitfalls in data visualization can prevent misinterpretation. Some frequent mistakes include:
- Inappropriate Chart Selection: Selecting the wrong type of chart can obscure the data’s story. For instance, using a pie chart for data that should be displayed as a time series can lead to confusion.
- Ignoring Data Integrity: Presenting manipulated or cherry-picked data can significantly skew the message and lead to distrust.
- Overly Complex Visuals: Complex visualizations can overwhelm viewers, detracting from the intended message. Strive for straightforward and digestible formats.
The effectiveness of a data visualization hinges not only on aesthetics but also on accuracy and clarity; these principles are essential for fostering understanding and informed decision-making.
Future Trends in Data Visualization
The field of data visualization is undergoing a transformative evolution as new technologies and methodologies emerge. As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, the demand for effective visualization tools is growing. This segment explores the future trends in data visualization, particularly focusing on how advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are reshaping the way we interpret complex datasets.
Emerging Technologies in Data Visualization
The incorporation of new technologies is revolutionizing the landscape of data visualization. Here are several key trends that are expected to define the future:
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): These immersive technologies are enabling users to interact with data in 3D environments, offering a more intuitive understanding of complex datasets. For example, organizations in industries like healthcare can visualize patient data in a spatial context, leading to better insights.
- Real-Time Data Visualization: As businesses increasingly operate in real-time environments, the ability to visualize real-time data streams is becoming critical. This approach helps organizations react promptly to market changes and operational challenges.
- Interactive Dashboards: The shift towards more interactive dashboards allows users to explore data dynamically. This trend enables stakeholders to tailor visualizations to their specific needs, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is being integrated into data visualization tools, allowing users to query datasets using natural language. This makes data exploration more accessible, even for those without technical expertise.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Enhancements
The integration of AI and ML is significantly enhancing the capabilities of data visualization tools. These technologies not only streamline the visualization process but also uncover deeper insights. Key enhancements include:
- Automated Data Insights: AI algorithms can analyze large datasets and automatically generate visualizations that highlight trends and anomalies. For instance, AI can identify patterns in sales data and suggest visual formats that best represent this information.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning models can forecast future trends based on historical data. For example, businesses can visualize expected sales trajectories, helping them to make informed inventory decisions.
- Enhanced Data Filtering and Segmentation: AI can intelligently filter and segment data, allowing users to visualize only the most relevant information. This capability ensures that visualizations are not cluttered and remain focused on key insights.
Business Preparedness for Future Trends
To leverage the advancements in data visualization effectively, businesses must adopt a proactive approach. Preparation involves several strategic actions:
- Invest in Training: Equipping teams with the skills to use advanced visualization tools and methods is essential. Training programs should focus on both technical skills and data literacy to enhance comprehension and decision-making.
- Embrace Agile Methodologies: Adopting agile practices can help organizations respond quickly to changing visualization needs. This approach fosters collaboration among stakeholders and accelerates the delivery of actionable insights.
- Prioritize Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data is fundamental to effective visualization. Companies must invest in data governance practices to maintain high data quality standards.
- Stay Updated with Technology Trends: Keeping abreast of technological advancements in data visualization is crucial. Businesses should regularly evaluate new tools and techniques to remain competitive.