Key strategies for improving database security and compliance set the stage for understanding the vital role that robust data protection plays in our increasingly digital world. As organizations navigate a landscape rife with data breaches and cyber threats, the implications of inadequate database security can be severe, leading to financial losses and reputational damage. High-profile breaches highlight the urgent need for effective strategies to safeguard sensitive information, ensuring compliance with regulations while fostering trust with customers.
In this exploration, we will delve into the common threats that databases face today and the innovative strategies that can be employed to enhance security. By identifying vulnerabilities and implementing strong authentication methods, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Regular security audits are essential, and aligning with compliance regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA not only protects data but also reinforces organizational integrity.
Importance of Database Security
In an era where data fuels business operations and decision-making, the significance of database security cannot be overstated. Organizations increasingly rely on vast amounts of sensitive information, making it critical to safeguard databases against unauthorized access, attacks, and breaches. The implications of failing to protect database security extend far beyond immediate financial losses, affecting reputation, customer trust, and regulatory compliance.Data breaches can lead to severe consequences for organizations, including monetary penalties, loss of sensitive customer information, and a tarnished public image.
The aftermath of such incidents often entails extensive remediation efforts, which can be both time-consuming and costly. An organization not only faces the direct costs associated with the breach but also experiences long-term impacts on stock price and customer loyalty.
High-Profile Database Security Breaches
Numerous high-profile database security breaches have demonstrated the dire consequences of inadequate database security measures. These incidents serve as cautionary tales for businesses worldwide, illustrating the need for robust protective strategies. One notable example is the Equifax breach in 2017, where sensitive information of approximately 147 million individuals was compromised. The breach exposed data such as social security numbers, birth dates, and addresses, leading to significant legal and financial repercussions for the company.
Equifax faced over $700 million in settlements, but the damage to its reputation was even more profound, resulting in diminished consumer trust.Another infamous case is the 2014 breach of Target, where hackers accessed credit and debit card information of approximately 40 million customers during the holiday shopping season. The breach not only cost Target over $200 million in settlements and legal fees but also caused a sharp decline in customer confidence, impacting sales for years to come.
These examples underline the importance of implementing comprehensive database security measures that include encryption, regular security audits, and employee training, among others. The repercussions of neglecting database security can resonate across an organization, affecting not just the immediate targets of the attack but also the broader business ecosystem.
Common Threats to Database Security
As organizations increasingly rely on databases to store sensitive information, understanding the common threats to database security becomes paramount. These threats not only jeopardize data integrity and confidentiality but also pose significant risks to compliance with regulatory standards. Various threats endanger databases, often exploiting vulnerabilities through sophisticated methods. Attackers are continually evolving their strategies, making it essential for organizations to stay informed about the potential risks.
The following sections delve into these threats and their implications for database security.
Types of Database Threats
Understanding the types of threats that target databases is crucial for implementing effective security measures. Below are several common threats that organizations face:
- SQL Injection: A prevalent attack method where malicious SQL code is inserted into queries. It allows attackers to manipulate databases, gaining unauthorized access or extracting sensitive data.
- Malware Attacks: Malicious software aimed at corrupting or stealing data from databases. This can include ransomware, which encrypts data and demands payment for decryption.
- Unauthorized Access: Occurs when individuals gain access to databases without permission, often exploiting weak credentials or unpatched vulnerabilities.
- Data Breaches: Incidents where sensitive data is accessed and exfiltrated by attackers, often leading to significant financial and reputational damage.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with legitimate access may misuse their privileges to steal data or cause harm to the database.
Methods of Exploiting Database Vulnerabilities
Attackers employ various techniques to exploit the vulnerabilities in database systems. Awareness of these methods is essential for developing effective countermeasures:
- Phishing: Attackers may use deceptive emails to trick users into providing credentials, which can then be used to access databases.
- Brute Force Attacks: This method involves systematically guessing passwords until the correct one is found, allowing unauthorized access to databases.
- Exploiting Unpatched Software: Many attacks take advantage of known vulnerabilities in database management systems that have not been updated or patched.
Statistics Highlighting the Rise of Database Threats
The frequency and sophistication of database threats have been on the rise, making it imperative for organizations to take proactive measures. Recent research reveals alarming statistics regarding database security:
- According to the 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report by Verizon, 43% of breaches involving databases were attributed to external actors, highlighting the need for robust perimeter defenses.
- A recent study by IBM found that the average cost of a data breach in 2023 reached $4.45 million, with compromised databases being a significant factor in these incidents.
- Reports indicate that SQL injection remains one of the top attack vectors, accounting for approximately 30% of all web application attacks in the past year.
“Organizations must recognize that database security is not a one-time effort but a continual process of monitoring, updating, and refining security measures.”
Key Strategies for Enhancing Database Security
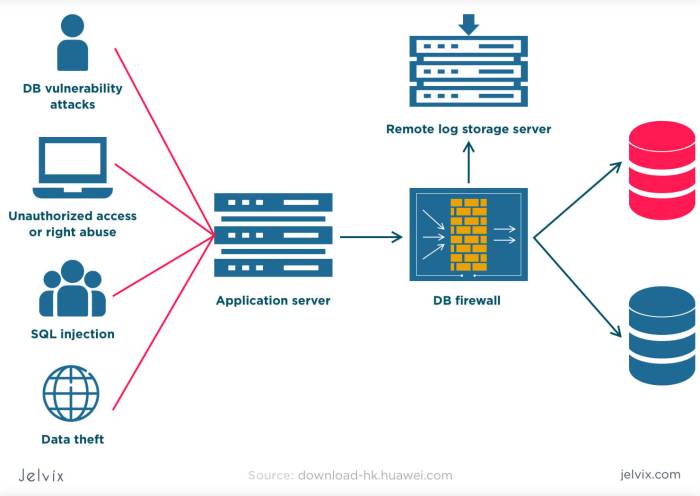
To safeguard sensitive information and maintain trust with stakeholders, organizations must prioritize robust database security measures. With the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, it has become imperative to adopt comprehensive strategies that protect databases from unauthorized access and data breaches.One of the most effective ways to enhance database security is through the implementation of best practices that focus on access control and permission management.
Protecting databases involves not only securing the data but also ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information. This can significantly mitigate the risk of data breaches and unauthorized actions within the database environment.
Best Practices for Securing Databases Against Unauthorized Access
Implementing best practices for database security is crucial for minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
Use Strong Password Policies
An effective database is only as reliable as its backup strategies. Therefore, understanding the best practices for database backup and recovery processes is essential. These practices not only safeguard your data but also ensure quick recovery in case of unexpected failures, allowing businesses to maintain continuity and minimize downtime.
Implement complex password requirements that include a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters, and mandate regular password changes.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Assign permissions based on user roles to ensure that individuals only have access to the data necessary for their job functions.
Data Encryption
Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest to ensure that unauthorized users cannot read the data, even if they gain access.
Regularly Update Database Software
Keep database management systems and related software up to date to protect against vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Checklist for Implementing Strong Authentication and Access Controls
Establishing a secure authentication framework is essential for controlling access to databases. Consider the following checklist to reinforce your database’s security posture:
Multi-Factor Authentication
Enable multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security beyond just passwords.
To truly evaluate the effectiveness of your business intelligence strategies, it’s crucial to focus on key metrics for measuring business intelligence success. This approach helps businesses identify what drives their decisions, ensuring they can pivot and adapt to market demands effectively. By analyzing these metrics, organizations can streamline operations and enhance overall performance.
Access Logs
Maintain logs of user access to monitor suspicious activity and facilitate audits.
Session Timeouts
Implement automatic session timeouts for inactive users to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
User Training
Provide regular training to employees on security best practices, including recognizing phishing attempts and securing personal credentials.
Importance of Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Periodic security audits and vulnerability assessments are critical for identifying and addressing potential weaknesses in database security. Regular audits help organizations ensure compliance with security policies and regulations, while also identifying areas for improvement. These assessments should involve both automated scanning tools and manual review processes to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the database security posture.
Identify Vulnerabilities
Routine assessments can uncover vulnerabilities that may remain undetected, enabling organizations to proactively address them.
Compliance Validation
Regular audits ensure adherence to industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS, which mandate strict data protection measures.
Enhanced Security Posture
Continuous improvement through regular reviews enhances overall database security, reducing the likelihood of successful cyber attacks.
“Proactive database security measures not only protect sensitive information but also build a foundation of trust with customers and stakeholders.”
Compliance Frameworks and Regulations

Compliance with data protection regulations is paramount for organizations that handle sensitive information. These regulations are designed to ensure that data privacy and security are prioritized, thereby protecting the rights of individuals while minimizing risks associated with data breaches. Understanding major compliance frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is essential for enhancing database security.Compliance regulations often dictate specific requirements that organizations must follow to protect sensitive information.
Aligning database security practices with these regulations not only helps mitigate legal risks but also strengthens overall data security posture. Below is an overview of major compliance regulations that affect database security.
Major Compliance Regulations Impacting Database Security, Key strategies for improving database security and compliance
Several pivotal regulations govern how organizations must secure their databases. The following table Artikels key compliance frameworks, their primary requirements, and their relevance to database security:
| Regulation | Primary Focus | Key Requirements | Relevance to Database Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Data Protection and Privacy | Consent, Right to Access, Data Breach Notifications | Requires robust access controls and encryption to safeguard personal data. |
| HIPAA | Healthcare Data Privacy | Patient Privacy, Security Rule, Breach Notification Rule | Mandates implementation of safeguards to protect electronic health information. |
| PCI DSS | Payment Card Data Security | Encryption, Access Control, Monitoring | Ensures protection of credit card information through stringent security measures. |
| CCPA | Consumer Privacy | Data Access, Deletion Rights, Non-Discrimination | Requires transparency in data collection and robust methods for data deletion. |
Aligning database security practices with compliance mandates involves a thorough understanding of each regulation’s requirements and implementing corresponding security measures. Organizations should conduct regular audits and assessments to ensure compliance is maintained. To enhance database security, the following strategies can be implemented in line with compliance frameworks:
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Implement role-based access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive databases.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic compliance audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and rectify potential security gaps.
- Training and Awareness: Educate employees about compliance requirements and best practices for data security to foster a culture of awareness.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and maintain an incident response plan to efficiently handle data breaches and comply with notification requirements.
By embedding these strategies within the organization’s operational framework, compliance with data protection regulations becomes a more manageable and integral aspect of database security.
Future Trends in Database Security: Key Strategies For Improving Database Security And Compliance

The landscape of database security is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing complexity of cyber threats. As organizations continue to migrate towards cloud environments and embrace digital transformation, understanding future trends in database security has become essential for safeguarding sensitive information. This segment explores the emerging technologies that promise to enhance database security, compares traditional security measures with innovative solutions like artificial intelligence and machine learning, and discusses the impact of cloud computing on database security strategies.
Emerging Technologies Enhancing Database Security
The integration of new technologies is reshaping the database security landscape, enabling organizations to stay ahead of potential threats. Technologies such as blockchain, AI, and machine learning are being leveraged to enhance security protocols. Each of these technologies offers unique advantages, including improved data integrity, real-time threat detection, and automated responses to security incidents.
- Blockchain Technology: By providing a decentralized and immutable ledger, blockchain enhances data integrity and ensures that unauthorized changes can be detected promptly. This technology is particularly beneficial in industries where trust and data provenance are paramount.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify anomalies that may indicate a security breach. This proactive approach allows organizations to respond to threats before they escalate.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning models can adapt to evolving threats by learning from historical data patterns. This adaptability enables organizations to refine their security measures continuously.
Comparison of Traditional Security Measures and Innovative Solutions
Traditional database security measures, such as firewalls and encryption, have served their purpose in protecting data. However, they often lack the agility and intelligence required to combat sophisticated cyber threats. In contrast, innovative solutions like AI and machine learning provide a dynamic approach to security that enhances the effectiveness of traditional measures.
“The combination of traditional security frameworks with advanced technologies significantly improves the overall defense posture of database systems.”
The shift from reactive to proactive security approaches is evident in the following comparisons:
- Threat Detection: Traditional methods rely on signature-based detection, while AI-driven solutions offer behavior-based detection that can identify new, unknown threats.
- Incident Response: Manual responses to security incidents can lead to delays; however, automated systems powered by AI can react instantly, minimizing damage.
- Scalability: As organizations grow, traditional security measures may struggle to keep up, whereas AI and machine learning solutions can easily scale to handle increased data loads and complexity.
Impact of Cloud Computing on Database Security Strategies
The adoption of cloud computing has revolutionized how organizations store and manage data, but it also introduces new security challenges. As more businesses transition to cloud environments, database security strategies must adapt to ensure compliance and protection against emerging threats.The shared responsibility model in cloud security necessitates collaboration between cloud service providers and users. Organizations must understand their role in safeguarding data while leveraging the security measures offered by cloud providers.
This includes implementing robust access controls, conducting regular security assessments, and utilizing advanced encryption techniques.
“Cloud computing shifts the focus of database security from solely protecting data at rest to ensuring security throughout its lifecycle, from creation to deletion.”
In conclusion, the future of database security hinges on the integration of innovative technologies and a strategic approach to cloud computing. Organizations that stay abreast of these trends will be better positioned to protect their valuable data assets in an increasingly complex threat landscape.